Why Are Networking Cables Crucial in Today's Digital World

Networking cables form the foundation of digital communication, enabling devices to connect seamlessly. They support high-speed data transmission vital for modern applications. For example:
- DOCSIS 3.0 technology supports speeds of up to 1 gigabit per second.
- DOCSIS 3.1 technology delivers speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second.
- Globally, approximately 3.4 billion internet users rely on robust connectivity.
Structured cabling systems ensure reliability and scalability. These systems provide a standardized framework, allowing businesses to expand networks efficiently. Whether using a Cat5e cable, Cat6 cable, Cat6a cable, or the latest Cat7 cable, reliable networking Cables enhance digital infrastructure stability.
Key Takeaways
- Networking cables are important for steady digital communication. They help send data quickly for things like video calls and cloud storage.
- Spending on organized cabling systems improves network growth and flexibility. This helps businesses expand without losing speed or quality.
- Fiber optic cables are the future of networks. They are super fast and efficient, which is needed for 5G and smart devices.
The Role of Networking Cables in Digital Communication

How Networking Cables Power Connectivity
Networking cables serve as the essential medium for transmitting data between devices, forming the backbone of digital communication. These cables enable seamless connectivity across various systems, from small home networks to large-scale enterprise setups. Their reliability ensures uninterrupted communication, which is vital for modern applications like video conferencing, cloud computing, and online gaming.
Recent advancements in cable technology have further enhanced their capabilities. Powered fiber cable systems, for instance, combine fiber-optic data transmission with copper low-voltage DC power connections. This integration allows up to 32 remote devices to connect from a single source, extending Power over Ethernet (PoE) distances significantly. Similarly, Fault-Managed Power System (FMPS) cables can deliver up to 2,000 watts of power over distances as long as 2 kilometers. These innovations support smart building applications, ensuring both safety and efficiency.
Undersea cables also play a critical role in global connectivity. They provide unparalleled capacity and low latency for data transmission, supporting essential services like financial transactions and national security. The increasing demand for these cables highlights their importance in sustaining global commerce and digital growth.
Tip: Networking cables are indispensable for maintaining reliable communication in both local and global networks. Their absence would halt digital connectivity, underscoring their vital role in the modern digital landscape.
Physical Infrastructure and Its Importance
The physical infrastructure of networking cables is fundamental to the stability and performance of digital systems. These cables form the physical layer of network architecture, ensuring data flows smoothly between devices. Metrics like uptime, fault tolerance, and scalability demonstrate the importance of robust physical setups in maintaining reliable connectivity.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Uptime | Frequency of network availability and proper functioning. |
| Consistency | Stability of network performance with minimal fluctuations. |
| Fault Tolerance | Ability to function despite failures in parts of the network. |
| Resilience | Capacity to recover quickly from disruptions, minimizing downtime. |
| Scalability | Ability to grow or adjust without sacrificing performance. |
| Packet Loss | Occurrence of data packets failing to reach their destination, affecting performance. |
| Latency | Time taken for data packets to travel from source to destination. |
| Jitter | Variation in packet arrival times, crucial for maintaining call quality. |
| Throughput | Amount of data transmitted over the network in a given time. |
| Error Rates | Frequency of data corruption or loss during transmission. |
| Recovery Time | Speed of network recovery after an issue occurs. |
| Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) | Average time between network failures, indicating reliability. |
Physical infrastructure also includes undersea cables, which are integral to global communications. These cables support critical services and economic activity, but their fragility has become a concern due to recent geopolitical conflicts. Protecting these cables is essential for maintaining economic stability and security.
ROXTONE specializes in providing high-quality networking cables that meet the demands of modern digital infrastructure. Their products ensure reliability, scalability, and adaptability, making them a trusted choice for businesses and individuals alike.
The Evolution of Networking Cables
Coaxial and Twisted Pair Cables: The Early Days
The journey of networking cables began with coaxial and twisted pair cables, which laid the foundation for modern connectivity. Coaxial cables, introduced in the 1970s, were widely used to connect personal computers. However, their lack of organization often resulted in chaotic network setups. Twisted pair cables emerged as a solution, offering better performance and reduced interference.
The 1980s marked a significant milestone with the introduction of structured cabling systems like the Premises Distribution System (PDS). These systems brought order and flexibility to network installations, enabling easier management and scalability. By the 1990s, the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) standardized cabling systems. This standardization led to the development of twisted-pair cables such as Cat 5e and Cat 6, which became the backbone of reliable and efficient networks.
- Timeline of Early Networking Cables:
- 1970s: Coaxial cables dominated, connecting personal computers.
- 1980s: Structured cabling systems like PDS improved organization.
- 1990s: Standardization of twisted-pair cables by TIA and EIA.
These early innovations paved the way for the advanced networking cables used today, ensuring seamless connectivity and scalability.
Ethernet Cables: Transforming Networking Standards
EtherNet Cables revolutionized networking by setting new benchmarks for speed, reliability, and performance. Introduced in the late 20th century, these cables quickly became the standard for local area networks (LANs). Their ability to support high-speed data transmission made them indispensable for both residential and commercial applications.
The evolution of Ethernet cables brought significant improvements in data transmission rates, frequency, and crosstalk reduction. For example:
| Ethernet Cable Type | Data Transmission Rate | Frequency | Crosstalk Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cat5e | Up to 1 Gb/s | 100 MHz | Improved |
| Cat6 | Up to 10 Gb/s | 250 MHz | Enhanced |
| Cat8 | Up to 40 Gb/s | 2000 MHz | Superior |
These advancements enabled Ethernet cables to meet the growing demands of modern applications, such as video streaming, online gaming, and cloud computing. Their versatility and reliability have made them a cornerstone of digital infrastructure.
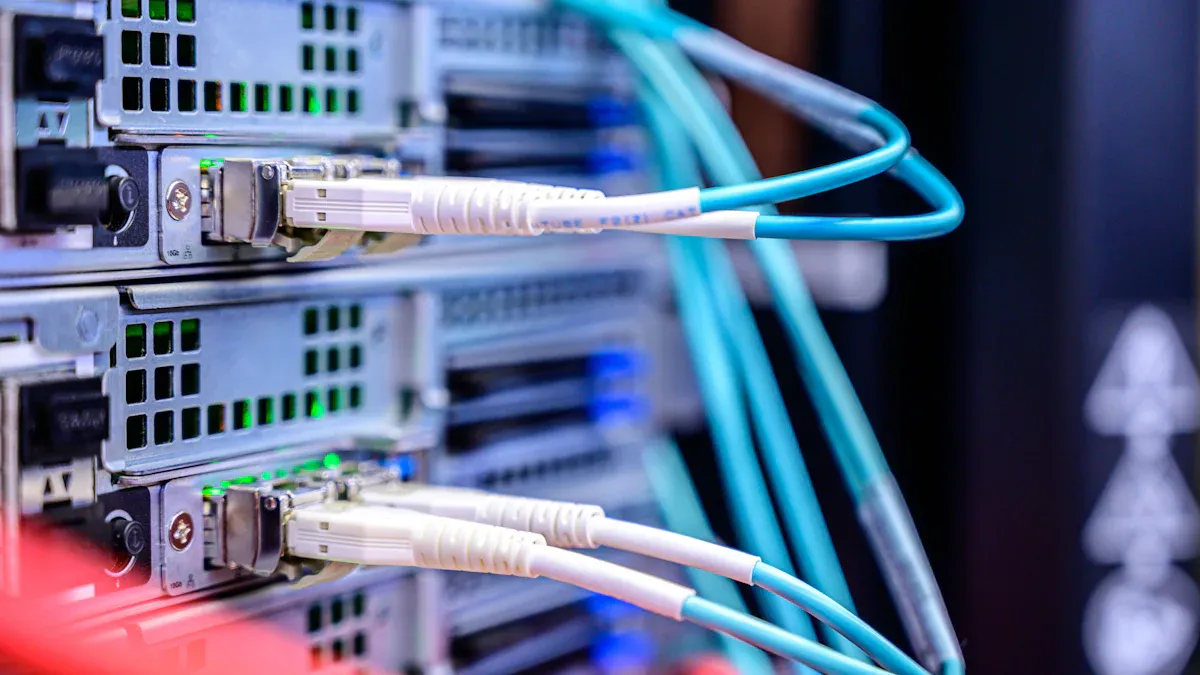
Fiber Optic Cables: A Technological Revolution
Fiber optic cables represent a groundbreaking leap in networking technology. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optics use light to transmit data, achieving unparalleled speed and efficiency. This innovation has transformed industries and enabled applications that were once unimaginable.
Fiber optic cables offer several advantages:
- High Sensitivity and Monitoring: Fiber optic sensors enhance real-time monitoring, crucial for industries like healthcare and manufacturing.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: These sensors detect structural anomalies in critical infrastructure, preventing major issues.
- Renewable Energy Applications: Fiber optics optimize performance in wind and solar energy systems, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- IoT Integration: The convergence of fiber optics with IoT technologies facilitates smarter, data-driven decision-making.
| Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity and Monitoring | Fiber optic sensors enhance sensitivity and real-time monitoring capabilities. |
| Market Growth Prediction | The global fiber optic market is projected to reach USD 2.53 billion by 2030. |
| Infrastructure Monitoring | Sensors detect structural anomalies in critical infrastructure. |
| Renewable Energy Applications | Fiber optics optimize performance in renewable energy sectors. |
| IoT Integration | Fiber optics enable smarter, data-driven decision-making processes. |
The adoption of fiber optic cables continues to grow, driven by their ability to support high-speed data transmission and advanced applications. As industries embrace technologies like 5G and IoT, fiber optics will remain at the forefront of innovation.
Applications and Benefits of Networking Cables
Reliable Connectivity for Critical Systems
Networking cables ensure reliable connectivity for systems that require uninterrupted performance. Industries like healthcare, finance, and transportation depend on stable networks to operate critical applications. Proper installation practices enhance reliability by preventing signal loss and physical damage. For example, regular inspections and protective routing safeguard cables from wear and environmental hazards. Adhering to standards, such as maintaining recommended cable lengths, further minimizes risks.
Organizations can improve network reliability by using signal boosters for long-distance connections and designing layouts that optimize cable placement. These measures reduce maintenance costs and ensure consistent performance. Structured cabling systems also simplify troubleshooting, allowing quick identification and resolution of issues.
Tip: Protecting cables from physical damage and environmental hazards is essential for maintaining reliable connectivity in critical systems.
High-Speed Data Transmission for Modern Needs
Modern networking cables support high-speed data transmission, meeting the demands of applications like video streaming, cloud computing, and IoT. Fiber optic cables, in particular, excel in delivering rapid data transfer rates. A study using OECD panel data from 32 countries (2000–2021) revealed that investments in high-speed infrastructure are influenced by regulatory policies. Strict net neutrality regulations can hinder these investments, highlighting the importance of fostering innovation-friendly environments.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Study Focus | Impact of net neutrality regulations on fiber-optic cable investments |
| Data Source | OECD panel data set for 32 countries (2000–2021) |
| Methodology | Various panel estimation techniques, including instrumental variables |
| Key Finding | Strict net neutrality regulations negatively impact investments in high-speed infrastructure |
Networking cables like Cat6 and Cat8 provide enhanced frequency and crosstalk reduction, ensuring smooth data transmission. These advancements enable faster communication and improved user experiences across industries.
Scalability and Adaptability in Expanding Networks
Networking cables offer scalability and adaptability, making them ideal for expanding networks. Structured cabling systems allow organizations to modify and grow their infrastructure without compromising performance. This flexibility supports diverse applications, enabling seamless integration of new technologies.
Key benefits include cost-effectiveness and easy troubleshooting. While initial installation costs may be higher, structured cabling reduces long-term expenses by minimizing the need for frequent updates. Its organized design simplifies maintenance, ensuring networks remain efficient and reliable.
As technology evolves, adaptability becomes crucial. Organizations that prioritize scalable infrastructure can better handle future challenges, ensuring their networks align with advancements like 5G and IoT. Networking cables play a pivotal role in this process, supporting growth and innovation across industries.
Future Trends in Networking Cables

Innovations in Fiber Optic Technology
Fiber optic technology continues to redefine networking capabilities with its advanced specifications and performance metrics. The geometry of the core and cladding plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient data transmission. High-purity silica glass minimizes scattering, while the cladding’s slightly lower refractive index traps light effectively. Protective coatings further enhance durability, making fiber optics ideal for high-demand environments like data centers.
Performance metrics such as insertion loss and bandwidth capacity highlight the reliability of fiber optic cables. Even minor losses can impact efficiency, which is why rigorous testing ensures every link meets stringent standards. These innovations enable data centers to handle increasing workloads while maintaining optimal performance.
ROXTONE remains at the forefront of fiber optic technology, delivering solutions that meet the evolving needs of modern infrastructure. Their commitment to quality ensures reliable connectivity for critical applications.
Emerging Materials and Designs
The future of networking cables lies in the adoption of sustainable materials and innovative designs. Manufacturers are exploring recyclable and biodegradable materials to reduce environmental impact. Improved insulation techniques minimize energy loss, promoting energy-efficient networks. Hybrid cabling systems, combining fiber optics with enhanced copper solutions, offer cost-effective performance for diverse applications.
Emerging designs also prioritize durability and adaptability. Smart cables equipped with fiber optic sensors provide real-time data on temperature and strain, making them suitable for harsh environments. Robotics and automation in cable installation enhance precision, reducing human error and improving efficiency.
These advancements align with global efforts to create sustainable and long-lasting infrastructure. Networking cables are evolving to meet the demands of modern systems while minimizing their ecological footprint.
Networking Cables in 5G and Beyond
The rollout of 5G networks has accelerated the demand for high-performance networking cables. Fiber optic technology, with its unmatched bandwidth capacity and minimal signal loss, plays a pivotal role in supporting 5G infrastructure. Wave division multiplexing (WDM) further expands the data-carrying capacity of optical fibers, enabling up to 40 wavelengths and potential future support for 128 channels.
Networking cables are also adapting to integrate seamlessly with IoT devices and edge computing systems. These advancements ensure faster data processing and reduced latency, critical for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities. As industries embrace 5G and beyond, networking cables will continue to evolve, driving innovation and connectivity.
ROXTONE’s cutting-edge solutions are designed to support the demands of next-generation networks, ensuring scalability and reliability for future technologies.
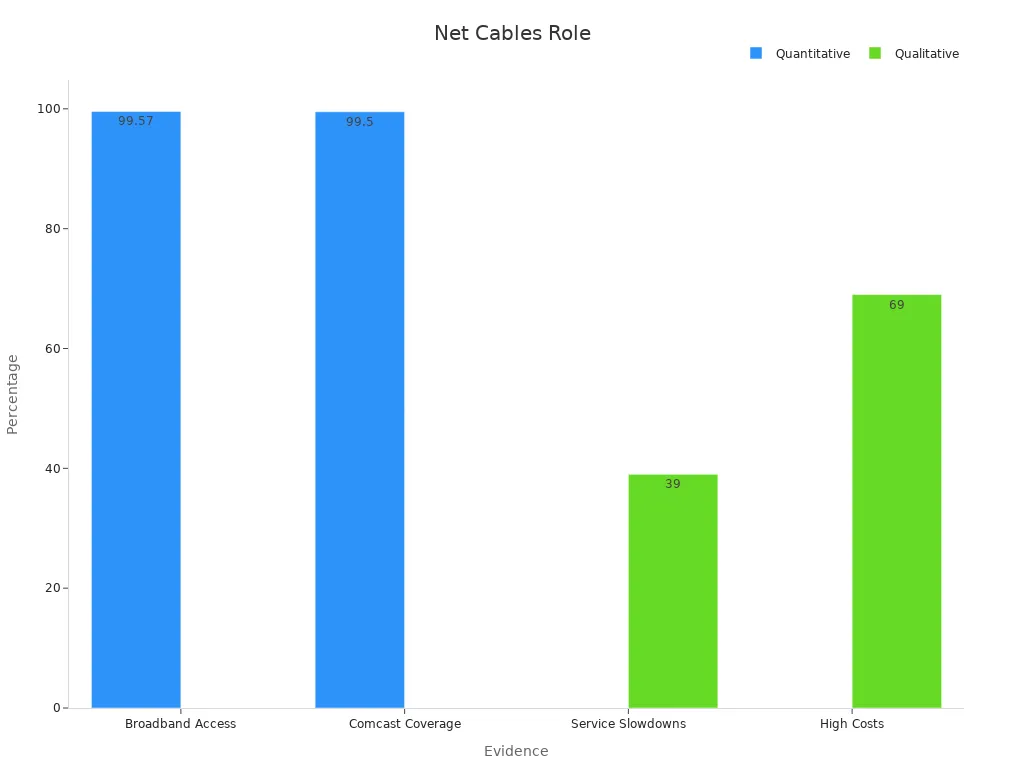
Networking cables form the backbone of digital infrastructure, ensuring reliable and high-speed connectivity. Quantitative evaluations reveal that 99.57% of addresses access broadband speeds above 100/20 Mbps, while qualitative surveys show 39% of users experience weekly slowdowns. These findings highlight their critical role in modern systems.
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Quantitative | 99.57% of addresses have access to broadband services with speeds above 100/20 Mbps. |
| Quantitative | 99.5% of residential and business addresses are served by Comcast, indicating limited competition. |
| Qualitative | 39% of survey respondents reported experiencing slowdowns or drops in service weekly. |
| Qualitative | 69% of respondents who were not 'very satisfied' indicated that service costs were too high. |
ROXTONE continues to innovate, delivering solutions that meet the demands of evolving digital infrastructure.
FAQ
What are the main types of networking cables?
Networking cables include coaxial, twisted pair, Ethernet (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6), and fiber optic cables. Each type serves specific connectivity and performance needs.
How do fiber optic cables differ from Ethernet cables?
Fiber optic cables use light for data transmission, offering higher speeds and longer distances. Ethernet cables rely on electrical signals and are ideal for shorter connections.
Why is structured cabling important for businesses?
Structured cabling simplifies network management, enhances scalability, and reduces maintenance costs. It ensures efficient performance and supports future technology upgrades.










